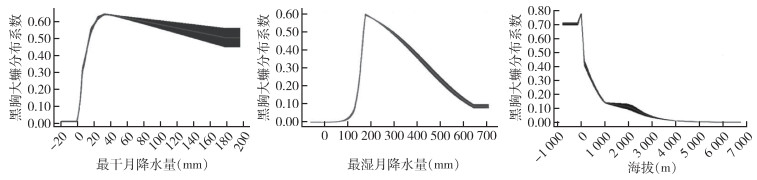
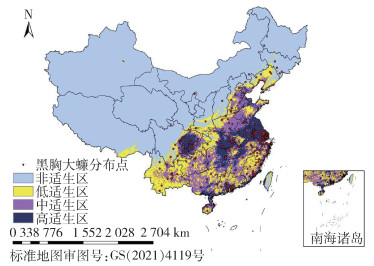
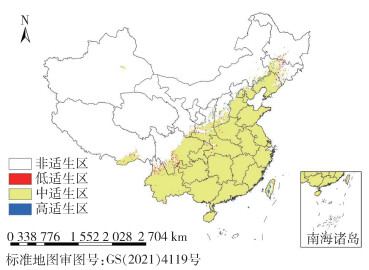
| 1 |
贺盼, 马强. 我国蜚蠊的分布及防制概况[J]. 医学动物防制, 2018, 34 (9):868-872.
|
|
He P, Ma Q. Distribution and control of cockroaches in China[J]. J Med Pest Control, 2018, 34 (9):868-872.
|
| 2 |
侯银续, 林浩飞, 王玮, 等. 安徽省黄山市2017-2018年室内蜚蠊监测结果分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2020, 31 (6):718-721.
DOI
|
|
Hou YX, Lin HF, Wang W, et al. An analysis of surveillance results of indoor cockroaches in Huangshan, Anhui province, China, 2017-2018[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2020, 31 (6):718-721.
DOI
|
| 3 |
侯银续, 水岩, 吴磊, 等. 蜚蠊的危害及防制技术研究进展[J]. 安徽预防医学杂志, 2021, 27 (6):487-491, 496.
DOI
|
|
Hou YX, Shui Y, Wu L, et al. Research progress on cockroach damage and control technology[J]. Anhui J Prev Med, 2021, 27 (6):487-491, 496.
DOI
|
| 4 |
孙耘芹, 李梅, 何凤琴, 等. 五种蜚蠊的生物学特性和综合治理[J]. 昆虫知识, 2004, 41 (3):216-222.
DOI
|
|
Sun YQ, Li M, He FQ, et al. Bionomics and integrated management of five species of cockroaches[J]. Entomol Knowl, 2004, 41 (3):216-222.
DOI
|
| 5 |
王韶华, 武峥嵘, 董腾飞, 等. 上海市嘉定区2017-2019年蟑螂侵害现状及居家灭蟑效果研究[J]. 上海预防医学, 2020, 32 (12):1001-1005.
DOI
|
|
Wang SH, Wu ZR, Dong TF, et al. Surveillance of cockroach population and evaluation of control effects in households from 2017 to 2019 in Jiading district of Shanghai[J]. Shanghai J Prev Med, 2020, 32 (12):1001-1005.
DOI
|
| 6 |
刘雪, 葛小伍, 梁丽, 等. 2017―2019年徐州市主城区主要病媒生物监测分析[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2021, 27 (2):124-128.
DOI
|
|
Liu X, Ge XW, Liang L, et al. Monitoring and analysis of the main vectors in main districts of Xuzhou from 2017 to 2019[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2021, 27 (2):124-128.
DOI
|
| 7 |
侯银续, 袁华玲, 陈李, 等. 黄山市蟑螂携带肠道菌种多样性初探[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2021, 27 (2):154-159.
DOI
|
|
Hou YX, Yuan HL, Chen L, et al. A preliminary study on the diversity of intestinal bacteria carried by cockroaches in Huangshan city[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2021, 27 (2):154-159.
DOI
|
| 8 |
赵泽芳, 卫海燕, 郭彦龙, 等. 人参潜在地理分布以及气候变化对其影响预测[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27 (11):3607-3615.
DOI
|
|
Zhao ZF, Wei HY, Guo YL, et al. Potential distribution of Panax ginseng and its predicted responses to climate change[J]. Chin J Appl Ecol, 2016, 27 (11):3607-3615.
DOI
|
| 9 |
姜志宽, 吴光华. 蟑螂防治(二): 蟑螂的生态习性与常见种类[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2009, 15 (2):169-172.
DOI
|
|
Jiang ZK, Wu GH. Cockroach control. Ⅱ: Ecological habits and common species of cockroaches[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2009, 15 (2):169-172.
DOI
|
| 10 |
Nasirian H. Infestation of cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) in the human dwelling environments: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Acta Trop, 2017, 167, 86-98.
DOI
|
| 11 |
张路. MaxEnt最大熵模型在预测物种潜在分布范围方面的应用[J]. 生物学通报, 2015, 50 (11):9-12.
|
|
Zhang L. The application of MaxEnt model in predicting the potential range of species[J]. Biol Bull, 2015, 50 (11):9-12.
|
| 12 |
Besprozvannykh VV, Ngo HD, Ha NV, et al. Descriptions of digenean parasites from three snail species, Bithynia fuchsiana (Morelet), Parafossarulus striatulus Benson and Melanoides tuberculata Müller, in North Vietnam[J]. Helminthologia, 2013, 50 (3):190-204.
DOI
|
| 13 |
Ren ZP, Wang DQ, Ma AM, et al. Predicting malaria vector distribution under climate change scenarios in China: Challenges for malaria elimination[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6 (1):20604.
DOI
|
| 14 |
王茹琳, 李庆, 封传红, 等. 基于MaxEnt的西藏飞蝗在中国的适生区预测[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37 (24):8556-8566.
DOI
|
|
Wang RL, Li Q, Feng CH, et al. Predicting potential ecological distribution of Locusta migratoria tibetensis in China using MaxEnt ecological niche modeling[J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2017, 37 (24):8556-8566.
DOI
|
| 15 |
周玉婷, 葛雪贞, 邹娅, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的长林小蠹的全球及中国适生区预测[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2022, 44 (11):90-99.
DOI
|
|
Zhou YT, Ge XZ, Zou Y, et al. Prediction of the potential geographical distribution of Hylurgus ligniperda at the global scale and in China using the MaxEnt model[J]. J Beijing For Univ, 2022, 44 (11):90-99.
DOI
|
| 16 |
曾权, 朱雪珍, 周利娟. 基于优化MaxEnt模型的南方三棘果在中国的潜在适生区预测[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2023, 44 (2):254-262.
|
|
Zeng Q, Zhu XZ, Zhou LJ. Prediction of potential suitable region for Emex australis in China based on the optimized MaxEnt mode[J]. J South China Agric Univ, 2023, 44 (2):254-262.
|
| 17 |
Wouyou HG, Lokonon BE, Idohou R, et al. Predicting the potential impacts of climate change on the endangered Caesalpinia bonduc (L.) Roxb in Benin (West Africa)[J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8 (3):e09022.
DOI
|
| 18 |
Liu D, Lei XD, Gao WQ, et al. Mapping the potential distribution suitability of 16 tree species under climate change in northeastern China using MaxEnt modelling[J]. J For Res, 2022, 33 (6):1739-1750.
DOI
|
| 19 |
戈斌, 黄涛, 张海兵, 等. 2011-2018年上海市奉贤区蟑螂监测分析[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2021, 27 (5):425-428.
DOI
|
|
Ge B, Huang T, Zhang HB, et al. Investigation on cockroaches in Fengxian district of Shanghai from 2011 to 2018[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2021, 27 (5):425-428.
DOI
|
| 20 |
徐绍锐, 汪世平, 吴仕筠, 等. 黑胸大蠊室内繁殖、发育的生物学特性研究[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2006, 22 (10):913-917.
DOI
|
|
Xu SR, Wang SP, Wu SJ, et al. Studies on biological characteristics of domestic reproduction and development of Periplaneta fuliginosa[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2006, 22 (10):913-917.
DOI
|
| 21 |
陈文锦, 袁高林. 宁德市蜚蠊种群密度与季节消长[J]. 海峡预防医学杂志, 2006, 12 (6):28-29.
DOI
|
|
Chen WJ, Yuan GL. Population density and seasonal fluctuation of cockroaches in Ningde city[J]. Strait J Prev Med, 2006, 12 (6):28-29.
DOI
|
| 22 |
李芮芝, 胡希军, 文亚峰, 等. 基于MaxEnt模型的丹霞梧桐生境预测模拟分析[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2022, 41 (6):1-7, 30.
DOI
|
|
Li RZ, Hu XJ, Wen YF, et al. Habitat prediction simulation analysis of Firmiana danxiaensis based on MaxEnt[J]. Chin Wild Plant Resour, 2022, 41 (6):1-7, 30.
DOI
|
| 23 |
沈培谊, 俞松青, 蔡昌曜, 等. 浙江省蜚蠊种群、地理分布特点及防制技术研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2001, 12 (4):275-281.
DOI
|
|
Shen PY, Yu SQ, Cai CY, et al. The study on the features of populations and distribution and control technique of the cockroach in Zhejiang province[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2001, 12 (4):275-281.
DOI
|
| 24 |
姜荣升. 基于CWRF研究我国降水变化及其与边界层高度的关系[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2021. DOI: 10.27248/d.cnki.gnjqc.2021.000035.
|
|
Jiang RS. Study the interaction between precipitation change and planetary boundary layer height based on CWRF[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2021. DOI: 10.27248/d.cnki.gnjqc.2021.000035.(in Chinese)
|
| 25 |
刘春蓁, 巢清尘, 王守荣, 等. 水文气象学领域的水文循环研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (1):1-10.
DOI
|
|
Liu CZ, Chao QC, Wang SR, et al. The research progress of hydrologic cycle in hydrometeorology[J]. Climate Change Res, 2023, 19 (1):1-10.
DOI
|