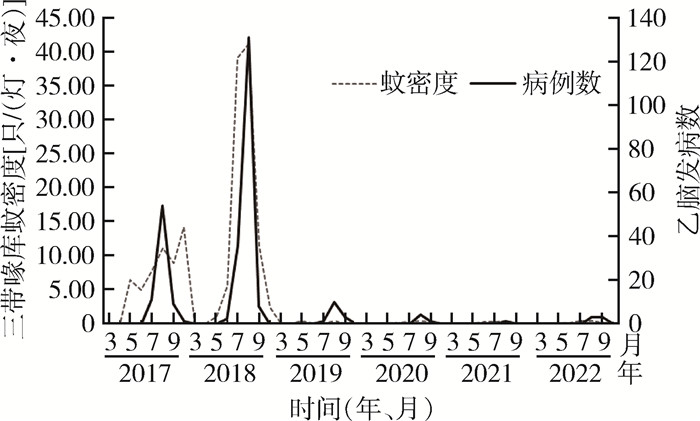
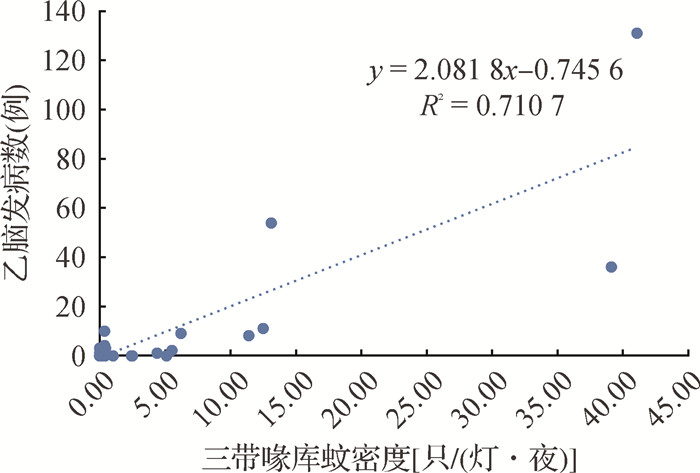
| 1 |
郭小连, 杨中华. 我国流行性乙型脑炎传播媒介的研究进展[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2019, 30 (1):106-110.
DOI
|
|
Guo XL, Yang ZH. Research progress in Japanese encephalitis vectors in China[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2019, 30 (1):106-110.
DOI
|
| 2 |
赵宁, 郭玉红, 吴海霞, 等. 2019年全国媒介蚊虫监测报告[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2020, 31 (4):395-400.
DOI
|
|
Zhao N, Guo YH, Wu HX, et al. National vector surveillance report on mosquitoes in China, 2019[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2020, 31 (4):395-400.
DOI
|
| 3 |
张伟, 邓良利, 刘竹, 等. 2015年成都市崇州乙脑媒介三带喙库蚊密度异常增高的应急控制[J]. 预防医学情报杂志, 2016, 32 (8):812-815.
|
|
Zhang W, Deng LL, Liu Z, et al. Emergency control for abnormal increase on density of Culex tritaeniorhynchus in Chongzhou of Chengdu in 2015[J]. J Prev Med Inf, 2016, 32 (8):812-815.
|
| 4 |
陈秋梅, 王热勤, 吴海霞, 等. 甘肃省天水市2017-2020年两种重要媒介蚊虫监测结果分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2021, 32 (4):456-460.
DOI
|
|
Chen QM, Wang RQ, Wu HX, et al. Surveillance results of two important vector mosquitoes in Tianshui, Gansu, China, 2017-2020[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2021, 32 (4):456-460.
DOI
|
| 5 |
刘其龙, 雷正龙, 赵彤言. 2008-2013年中国流行性乙型脑炎流行病学特征分析[J]. 寄生虫与医学昆虫学报, 2015, 22 (2):82-87.
|
|
Liu QL, Lei ZL, Zhao TY. Epidemiological characteristic analysis of Japanese encephalitis in China's mainland during 2008-2013[J]. Acta Parasitol Med Entomol Sin, 2015, 22 (2):82-87.
|
| 6 |
王晓军, 张彦平, 张荣珍, 等. 中国1998-2002年流行性乙型脑炎流行趋势分析[J]. 中国计划免疫, 2004, 10 (4):215-217.
DOI
|
|
Wang XJ, Zhang YP, Zhang RZ, et al. Analysis on epidemic trend of Japanese B encephalitis during 1998-2002 in China[J]. Chin J Vaccines Immun, 2004, 10 (4):215-217.
DOI
|
| 7 |
陈园生, 梁晓峰, 王晓军, 等. 中国2000-2004年流行性乙型脑炎流行病学特征分析[J]. 中国计划免疫, 2006, 12 (3):196-198.
DOI
|
|
Chen YS, Liang XF, Wang XJ, et al. Epidemiological analysis of the Japanese B encephalitis in China during 2000-2004[J]. Chin J Vaccines Immun, 2006, 12 (3):196-198.
DOI
|
| 8 |
吴丹, 尹遵栋, 李军宏, 等. 中国2014-2018年流行性乙型脑炎流行病学特征[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2020, 26 (1):1-4.
DOI
|
|
Wu D, Yin ZD, Li JH, et al. Epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis in China, 2014-2018[J]. Chin J Vacc Immun, 2020, 26 (1):1-4.
DOI
|
| 9 |
王志会, 李文, 郭玉红, 等. 2005-2019年中国北部8省市流行性乙型脑炎流行特征分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2021, 32 (2):197-203.
DOI
|
|
Wang ZH, Li W, Guo YH, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of Japanese encephalitis in eight provinces and municipalities of northern China, 2005-2019[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2021, 32 (2):197-203.
DOI
|
| 10 |
赵祥凯, 张晓曙, 崔旭东, 等. 甘肃省流行性乙型脑炎的流行病学特征和疾病负担分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2021, 25 (7):791-795.
DOI
|
|
Zhao XK, Zhang XS, Cui XD, et al. Analysis on the epidemiological characteristics and disease burden of Japanese encephalitis in Gansu province[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2021, 25 (7):791-795.
DOI
|
| 11 |
吴海霞, 鲁亮, 孟凤霞, 等. 2006-2015年我国蚊虫监测报告[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2017, 28 (5):409-414.
DOI
|
|
Wu HX, Lu L, Meng FX, et al. Reports on national surveillance of mosquitoes in China, 2006-2015[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2017, 28 (5):409-414.
DOI
|
| 12 |
刘小波, 吴海霞, 殷文武, 等. 2006-2012年全国19省三带喙库蚊监测研究[J]. 疾病监测, 2014, 29 (4):281-286.
DOI
|
|
Liu XB, Wu HX, Yin WW, et al. Surveillance for Culex tritaeniorhynchus in China, 2006-2012[J]. Dis Surveill, 2014, 29 (4):281-286.
DOI
|
| 13 |
农长挥, 蔡开祥, 梁亮. 2014-2015年靖西市乙脑蚊媒监测结果分析[J]. 应用预防医学, 2016, 22 (3):256-257, 260.
DOI
|
|
Nong CH, Cai KX, Liang L. Analysis of Japanese encephalitis mosquito vector surveillance results in Jingxi city from 2014 to 2015[J]. J Appl Prev Med, 2016, 22 (3):256-257, 260.
DOI
|
| 14 |
罗会平, 孙玲, 刘江云, 等. 2005-2019年云南省勐腊县流行性乙型脑炎流行特征分析[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2021, 27 (1):67-70.
DOI
|
|
Luo HP, Sun L, Liu JY, et al. Analysis on epidemiological characteristics of Japanese encephalitis in Mengla county of Yunnan from 2005 to 2019[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2021, 27 (1):67-70.
DOI
|
| 15 |
吕炜, 黄谊, 段丽琼, 等. 2007-2011年湖南省蚊媒传染病与蚊虫密度季节消长相关性分析[J]. 实用预防医学, 2012, 19 (11):1662-1664.
DOI
|
|
Lyu W, Huang Y, Duan LQ, et al. Analysis on correlation between mosquito-borne diseases and seasonal fluctuation of mosquito density in Hunan province from 2007 to 2011[J]. Pract Prev Med, 2012, 19 (11):1662-1664.
DOI
|
| 16 |
高文, 马丽华, 黄钢, 等. 河北省2013-2015年蚊媒传染病与蚊密度相关性分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2016, 27 (4):350-353.
DOI
|
|
Gao W, Ma LH, Huang G, et al. Analysis on correlation between mosquito-borne diseases and seasonality of mosquito density in Hebei province from 2013 to 2015[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2016, 27 (4):350-353.
DOI
|
| 17 |
高文, 黄钢, 韩晓莉. 基于蚊密度差分自回归移动平均模型预测流行性乙型脑炎的贝叶斯判别分析研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2018, 29 (6):557-563.
DOI
|
|
Gao W, Huang G, Han XL. Application of Bayes analysis in Japanese encephalitis prediction based on multiple seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average model[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2018, 29 (6):557-563.
DOI
|
| 18 |
戴德芳, 李放军, 蔡亮, 等. 湖南省流行性乙型脑炎流行特征及蚊媒监测结果分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2015, 26 (6):605-608.
DOI
|
|
Dai DF, Li FJ, Cai L, et al. Analysis of Japanese encephalitis epidemiology and comprehensive monitoring results in Hunan province[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2015, 26 (6):605-608.
DOI
|
| 19 |
王小军, 蔡玉成, 贾续珍, 等. 甘肃省陇南市流行性乙型脑炎疫情与蚊媒监测结果相关性分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2019, 30 (5):502-505.
DOI
|
|
Wang XJ, Cai YC, Jia XZ, et al. Correlation between Japanese encephalitis epidemic and mosquito vector surveillance results in Longnan, Gansu province, China[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2019, 30 (5):502-505.
DOI
|