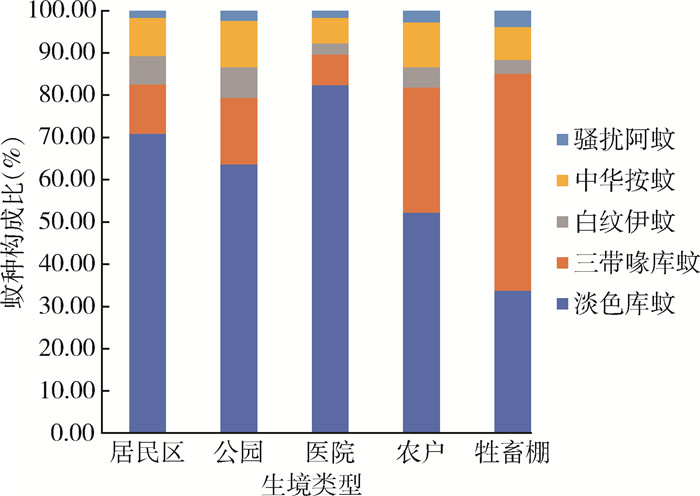
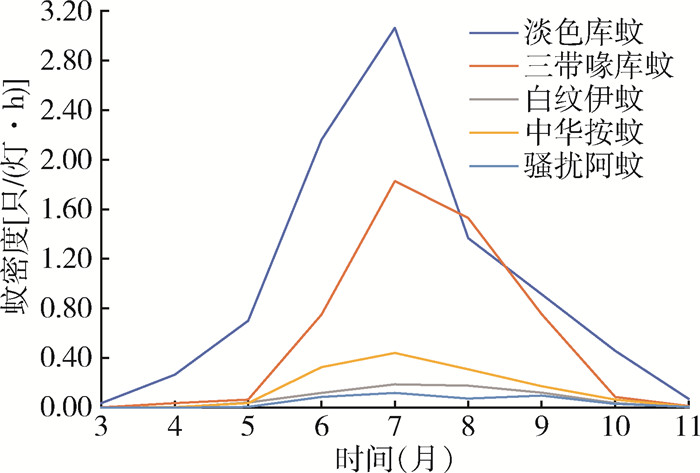
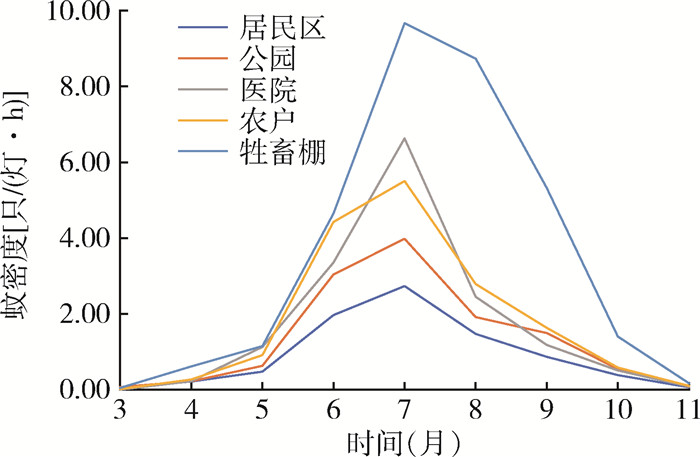
| 1 |
刘起勇. 新时代媒介生物传染病形势及防控对策[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2019, 30 (1):1-6, 11.
DOI
|
|
Liu QY. Epidemic profile of vector-borne diseases and vector control strategies in the new era[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2019, 30 (1):1-6, 11.
DOI
|
| 2 |
Bai L, Morton LC, Liu QY. Climate change and mosquito-borne diseases in China: A review[J]. Global Health, 2013, 9, 10.
DOI
|
| 3 |
蔡蓉, 邵宗贤, 苏琦, 等. 淮安市2017年蚊生态学及抗药性调查[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2019, 25 (2):116-118.
DOI
|
|
Cai R, Shao ZX, Su Q, et al. The ecology and insecticide resistance of mosquitoes in Huai'an city in 2017[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2019, 25 (2):116-118.
DOI
|
| 4 |
王巧燕, 王韶华, 武峥嵘, 等. 上海市嘉定区2018-2020年成蚊生态学监测研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2022, 33 (3):346-350.
DOI
|
|
Wang QY, Wang SH, Wu ZR, et al. Ecological surveillance of adult mosquitoes in Jiading district, Shanghai from 2018 to 2020[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2022, 33 (3):346-350.
DOI
|
| 5 |
赵宁, 郭玉红, 吴海霞, 等. 2019年全国媒介蚊虫监测报告[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2020, 31 (4):395-400.
DOI
|
|
Zhao N, Guo YH, Wu HX, et al. National vector surveillance report on mosquitoes in China, 2019[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2020, 31 (4):395-400.
DOI
|
| 6 |
杨维芳, 张育富, 刘大鹏, 等. 江苏省2008-2018年蚊虫种群消长研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2021, 32 (1):45-51.
DOI
|
|
Yang WF, Zhang YF, Liu DP, et al. A study of mosquito population variation in Jiangsu province, China, 2008-2018[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2021, 32 (1):45-51.
DOI
|
| 7 |
胡雅劼, 张镇川, 李玲玲, 等. 四川省2017-2021年成蚊生态学特征分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2023, 34 (1):44-47.
DOI
|
|
Hu YJ, Zhang ZC, Li LL, et al. Analysis of adult mosquito bionomic characteristics in Sichuan province, China, 2017-2021[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2023, 34 (1):44-47.
DOI
|
| 8 |
杨中华, 周红宁. 云南省三带喙库蚊生物学习性研究进展[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2018, 29 (4):403-406.
DOI
|
|
Yang ZH, Zhou HN. Progress on investigation of Culex tritaeniorhynchus biological habit in Yunnan province[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2018, 29 (4):403-406.
DOI
|
| 9 |
杨维芳, 孙俊, 徐燕, 等. 三带喙库蚊发生量与气象因子相关性初步分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2010, 21 (1):49-50.
|
|
Yang WF, Sun J, Xu Y, et al. A preliminary study on the relationship between occurrence of Culex tritaeniorhynchus and meteorological factors[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2010, 21 (1):49-50.
|
| 10 |
Chuang TW, Hildreth MB, Vanroekel DL, et al. Weather and land cover influences on mosquito populations in Sioux Falls, South Dakota[J]. J Med Entomol, 2011, 48 (3):669-679.
DOI
|
| 11 |
闫冬明, 黄坤, 赵春春, 等. 常用蚊虫监测方法和技术研究进展[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2020, 31 (1):108-112.
DOI
|
|
Yan DM, Huang K, Zhao CC, et al. Research advances in common methods and techniques for mosquito surveillance[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2020, 31 (1):108-112.
DOI
|
| 12 |
李旭龙, 张宝芳, 张铮, 等. 2006-2009年宝鸡市蚊虫密度及不同监测方法比较研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2010, 21 (6):592-595.
|
|
Li XL, Zhang BF, Zhang Z, et al. Study on the different methods of mosquito monitoring and its density in Baoji from 2006 to 2009[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2010, 21 (6):592-595.
|
| 13 |
马德珍, 明明, 陆华. 光催化诱蚊灯与BG-trap捕蚊器诱蚊效果比较研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2020, 31 (6):685-689.
DOI
|
|
Ma DZ, Ming M, Lu H. Mosquito-trapping effect of photocatalysis mosquito lamp versus BG-trap mosquito lamp[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2020, 31 (6):685-689.
DOI
|