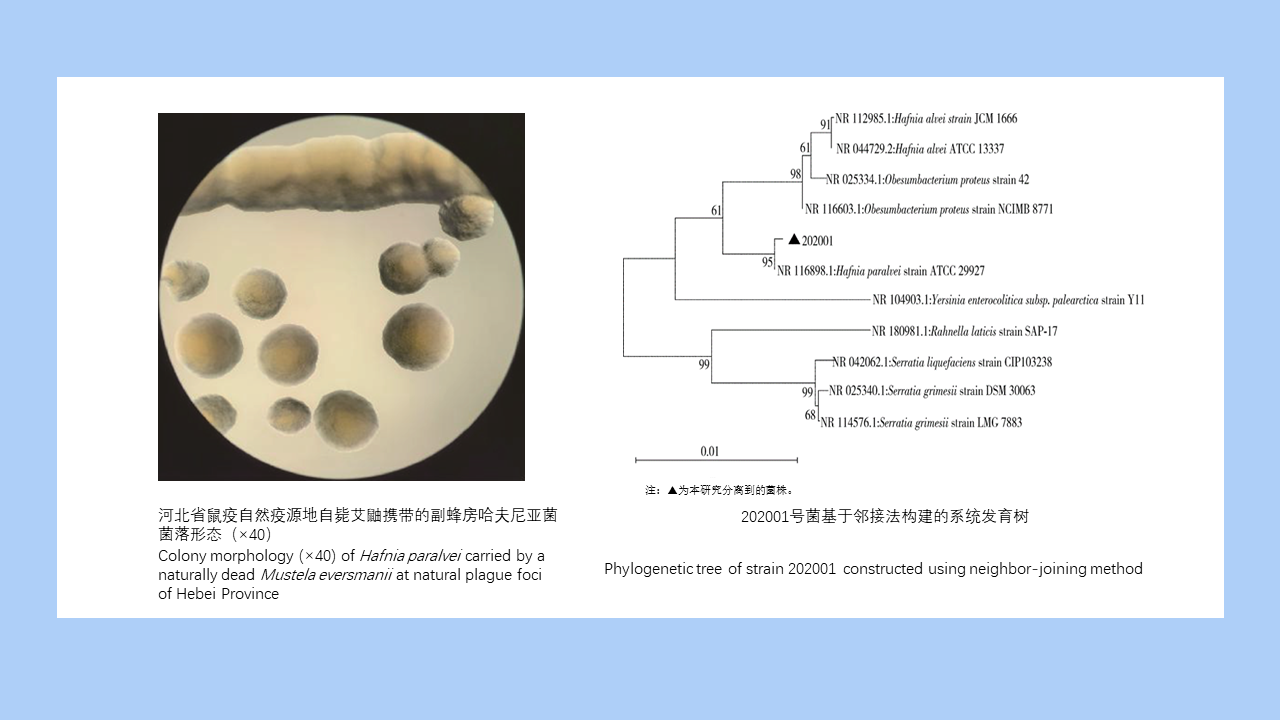
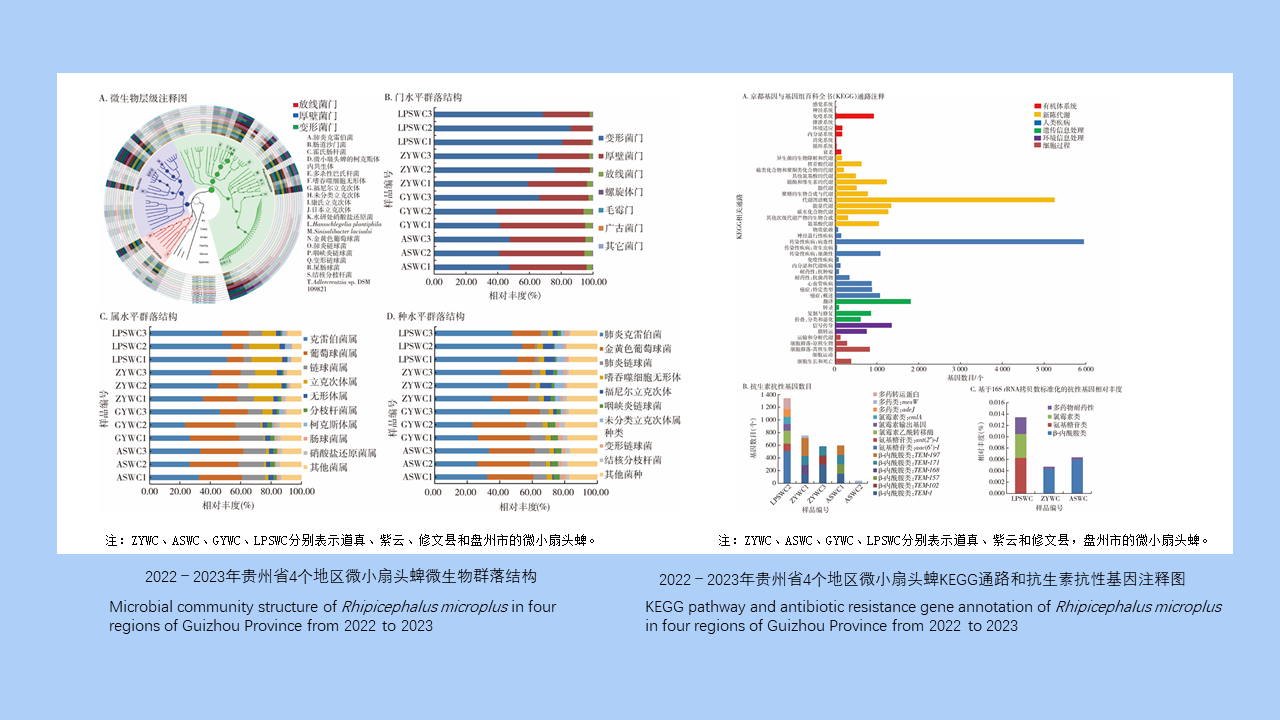
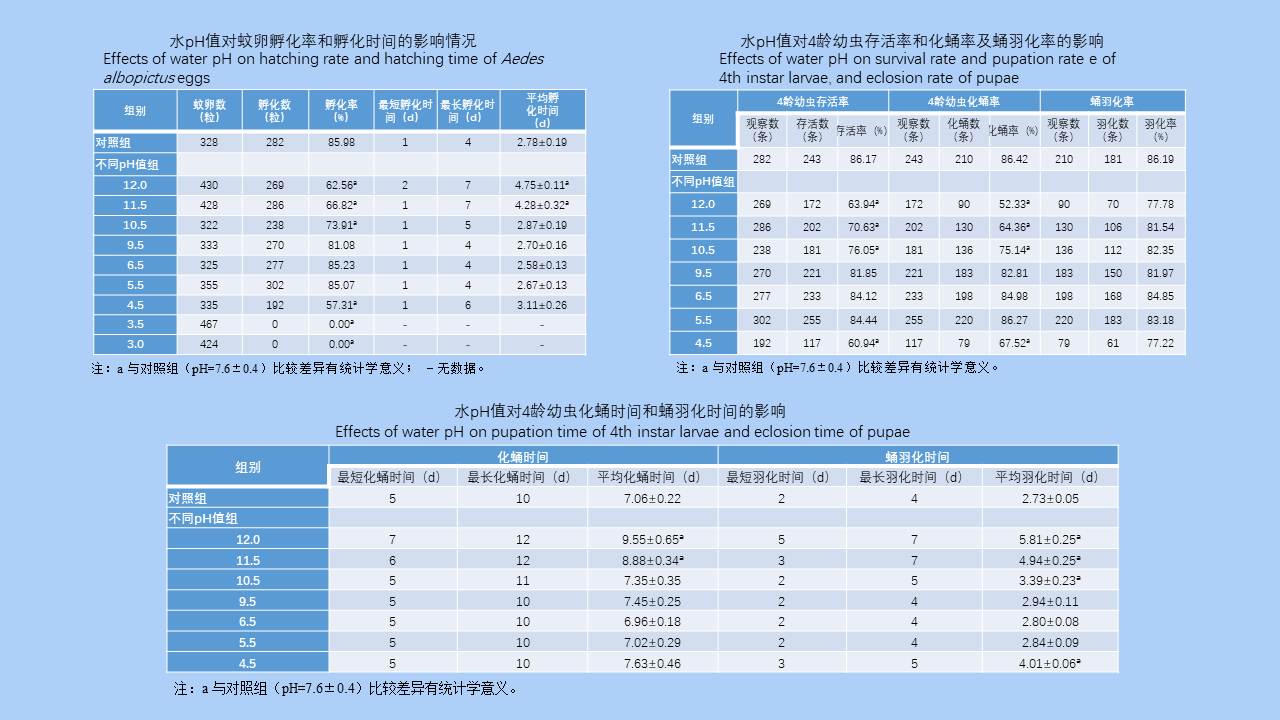
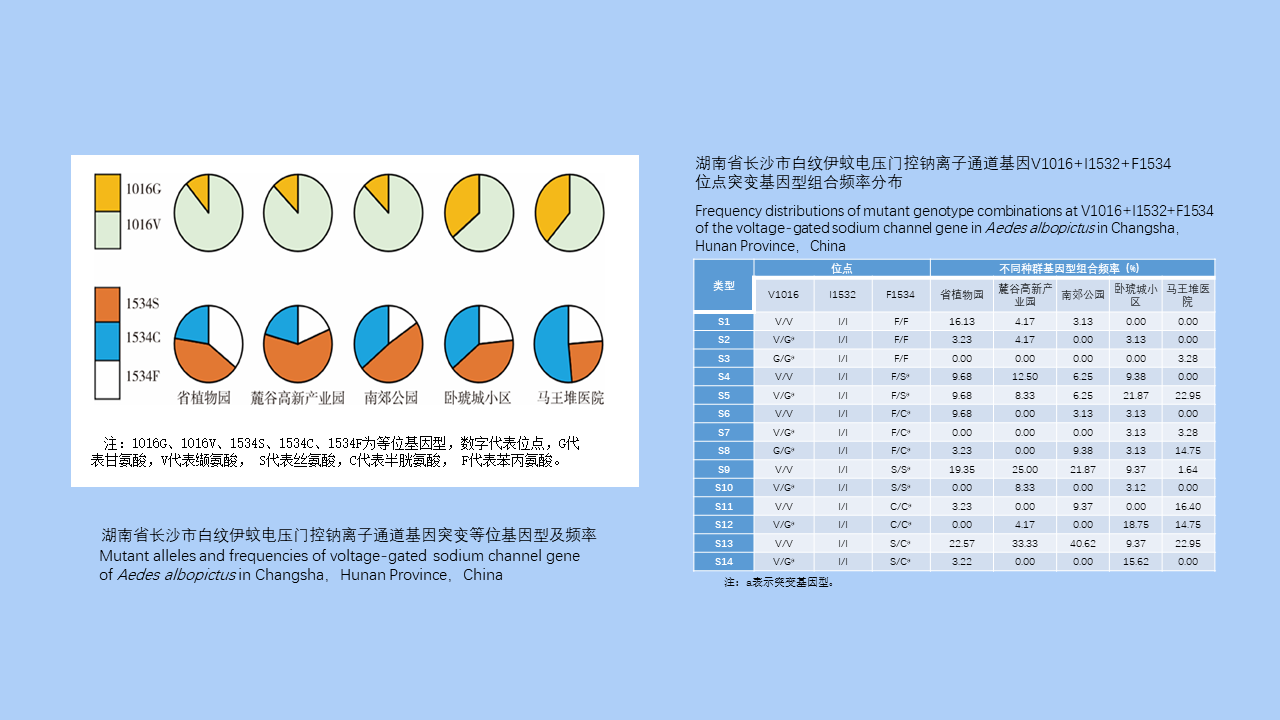
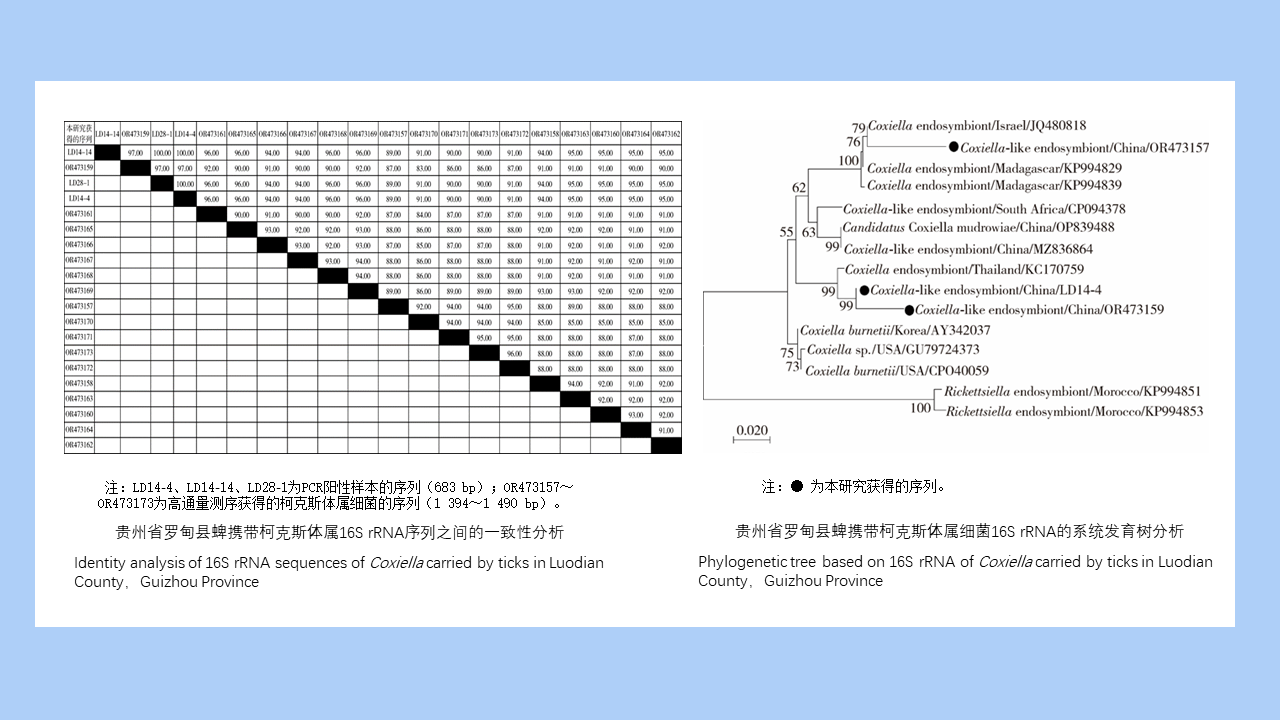
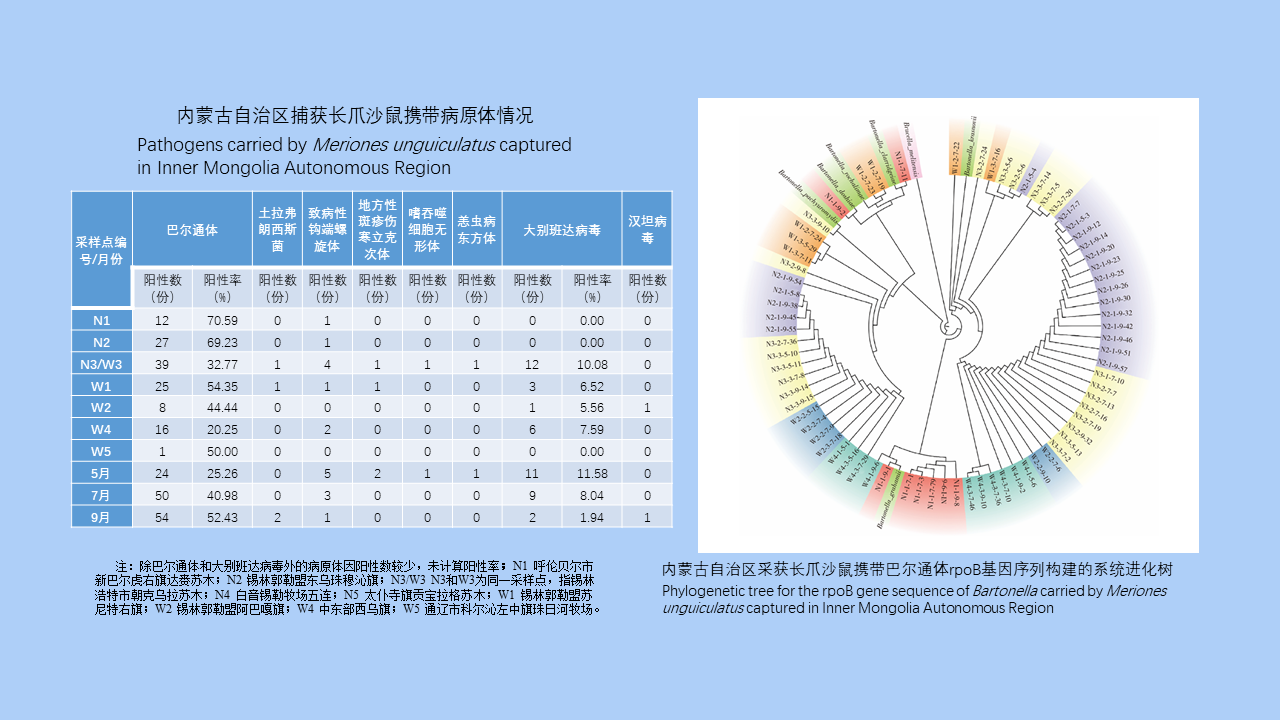
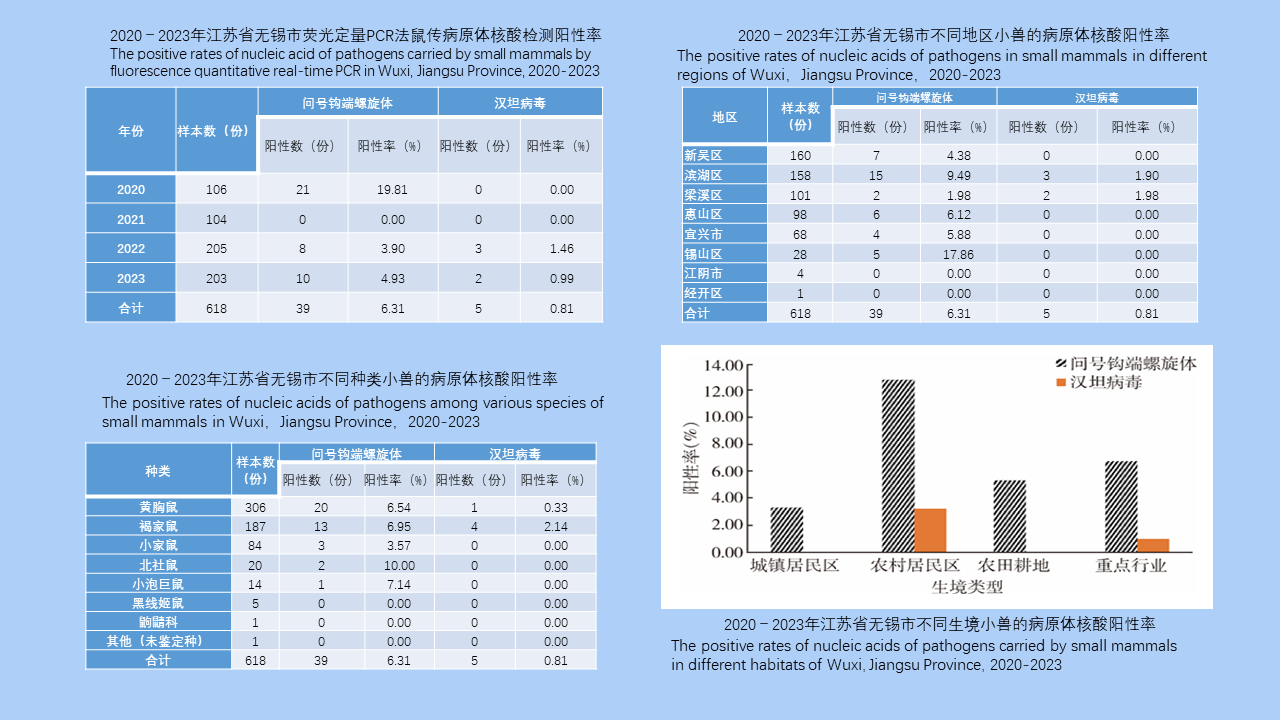
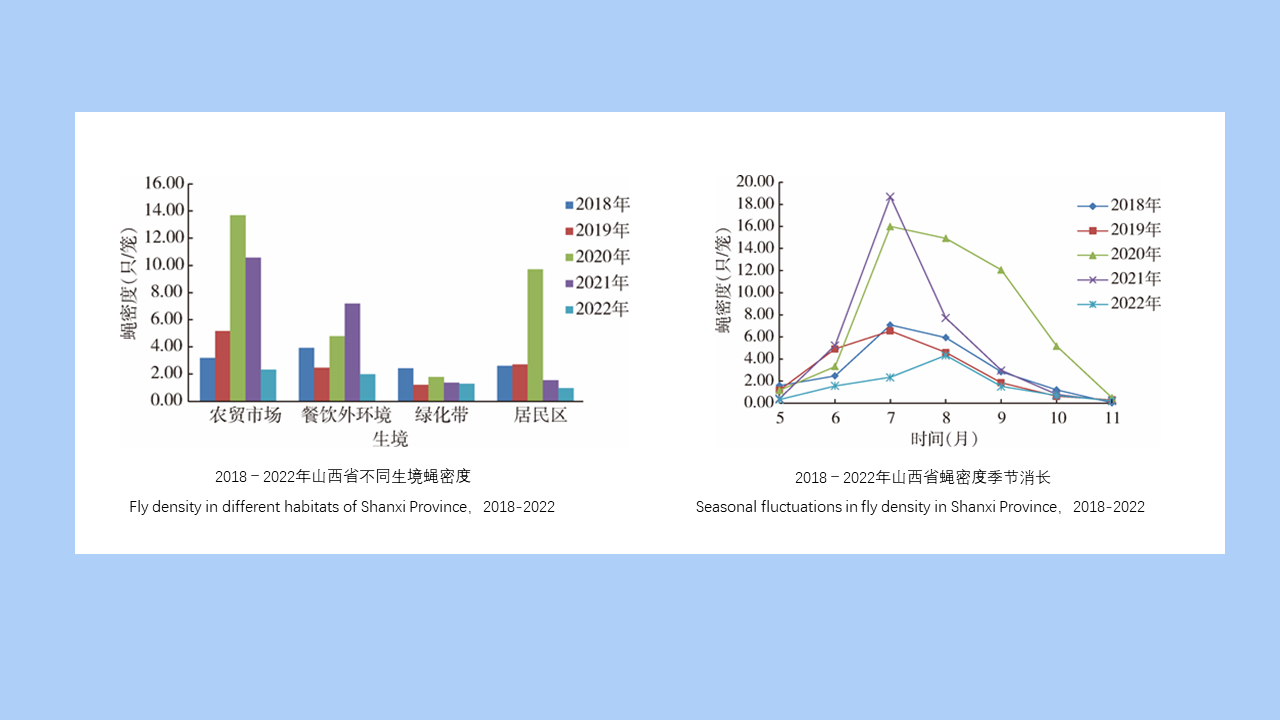
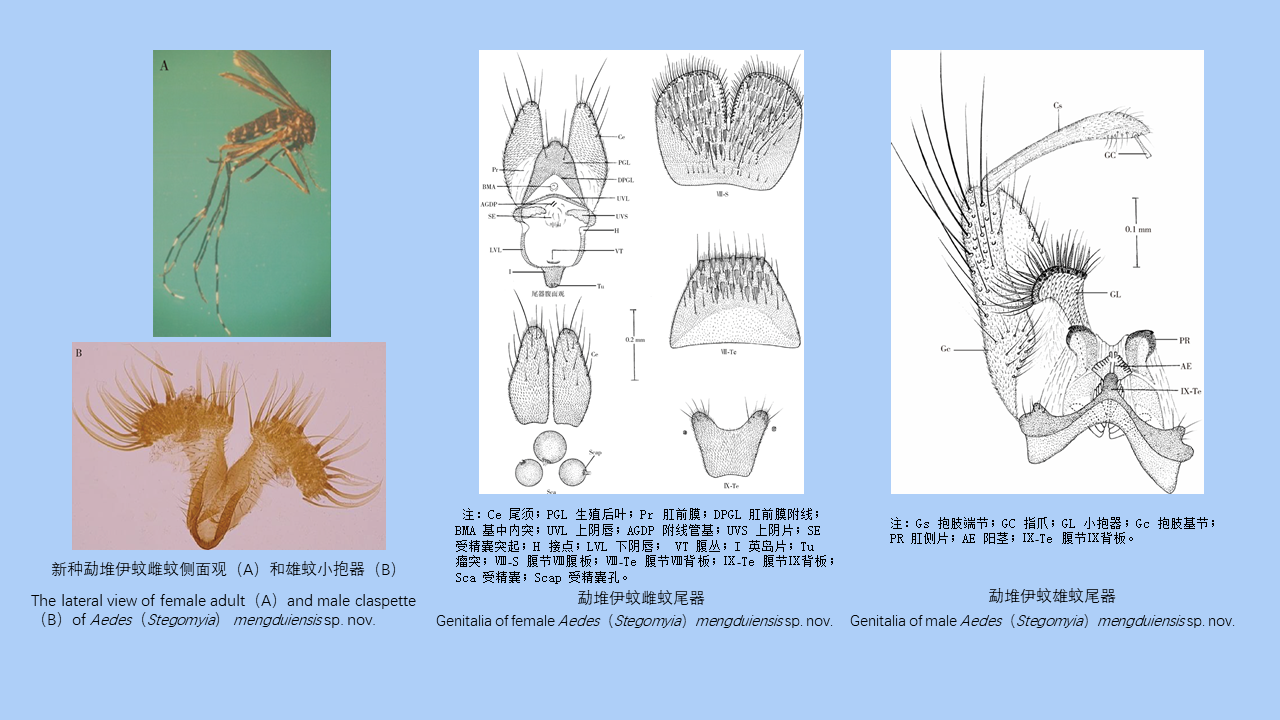
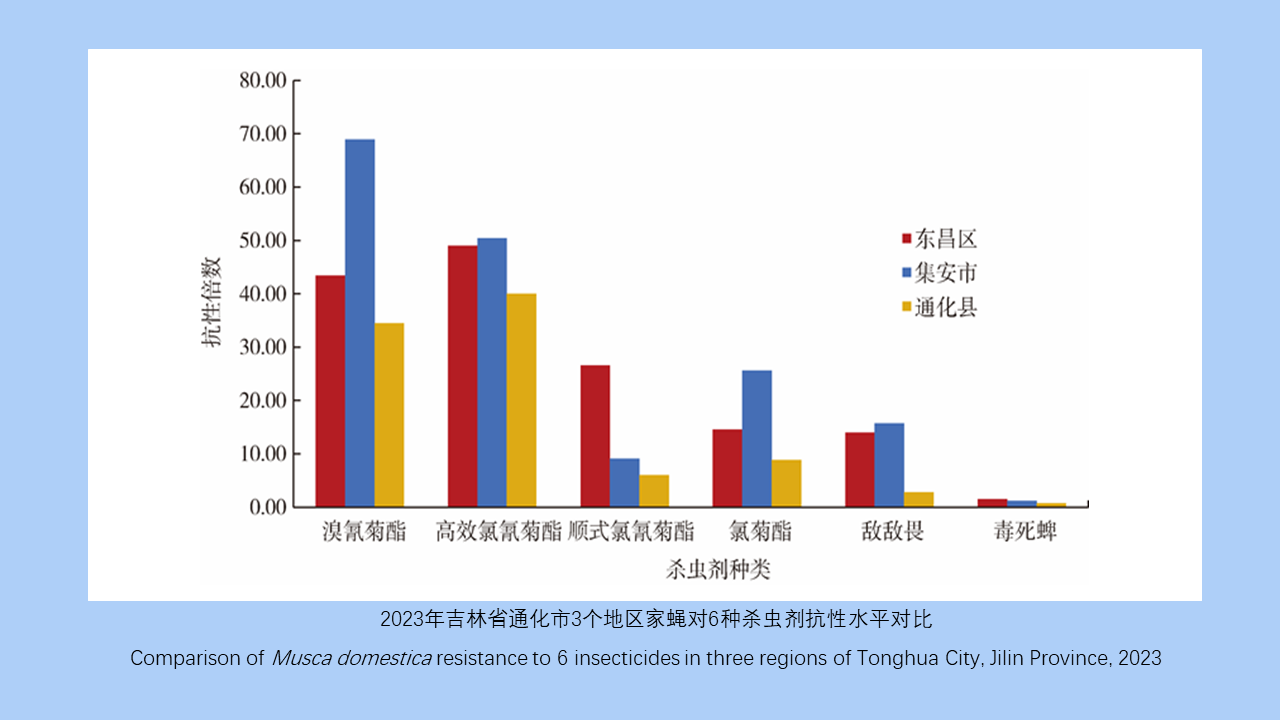
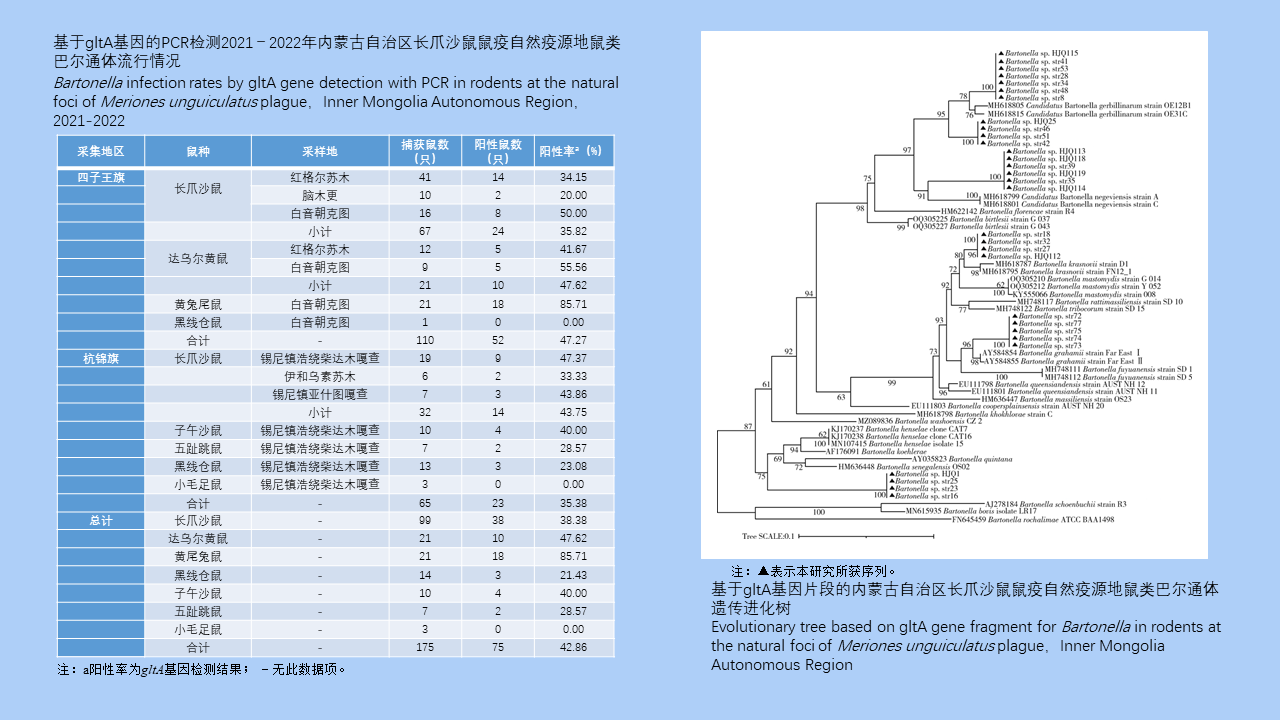
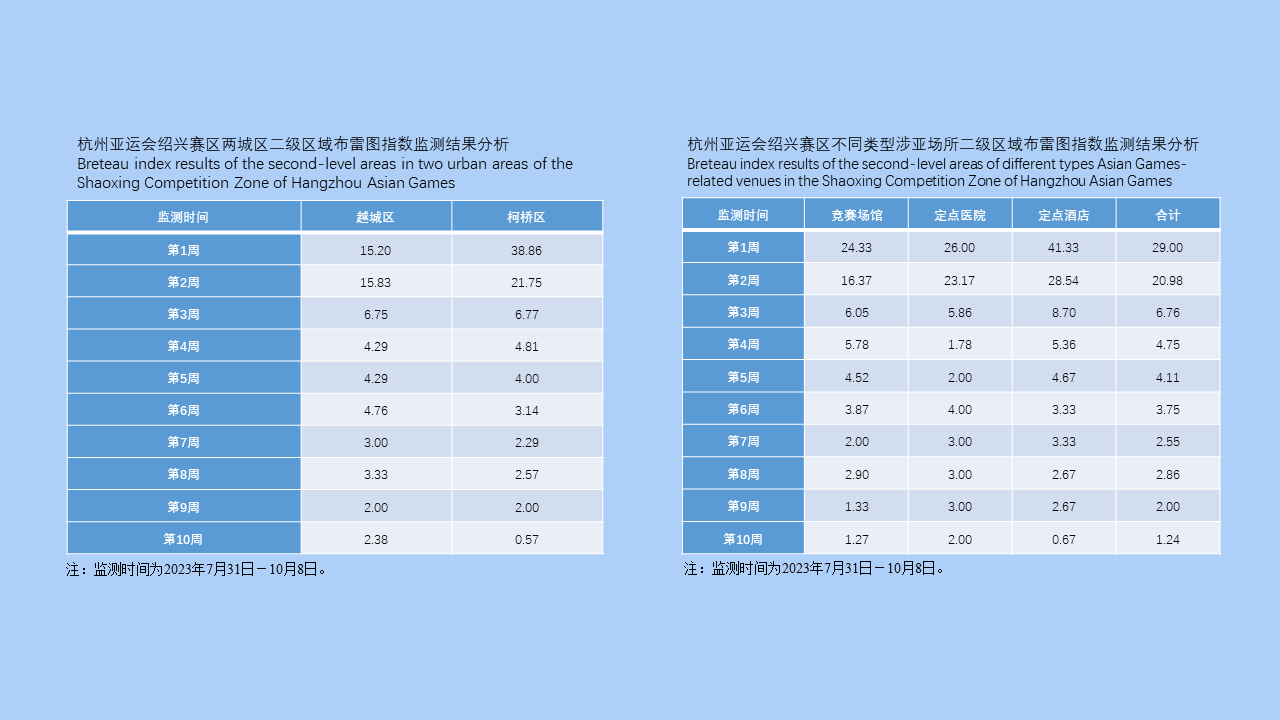
MO Li-juan, XU Jin-ping, LI Dong-mei, HUANG Li-ju, CHEN Ren-qiang, WU Nan-wei, LIU Ying, LIU Wu-han, YE Shu-ying, ZENG Xue-xia, SUN Ding-wei
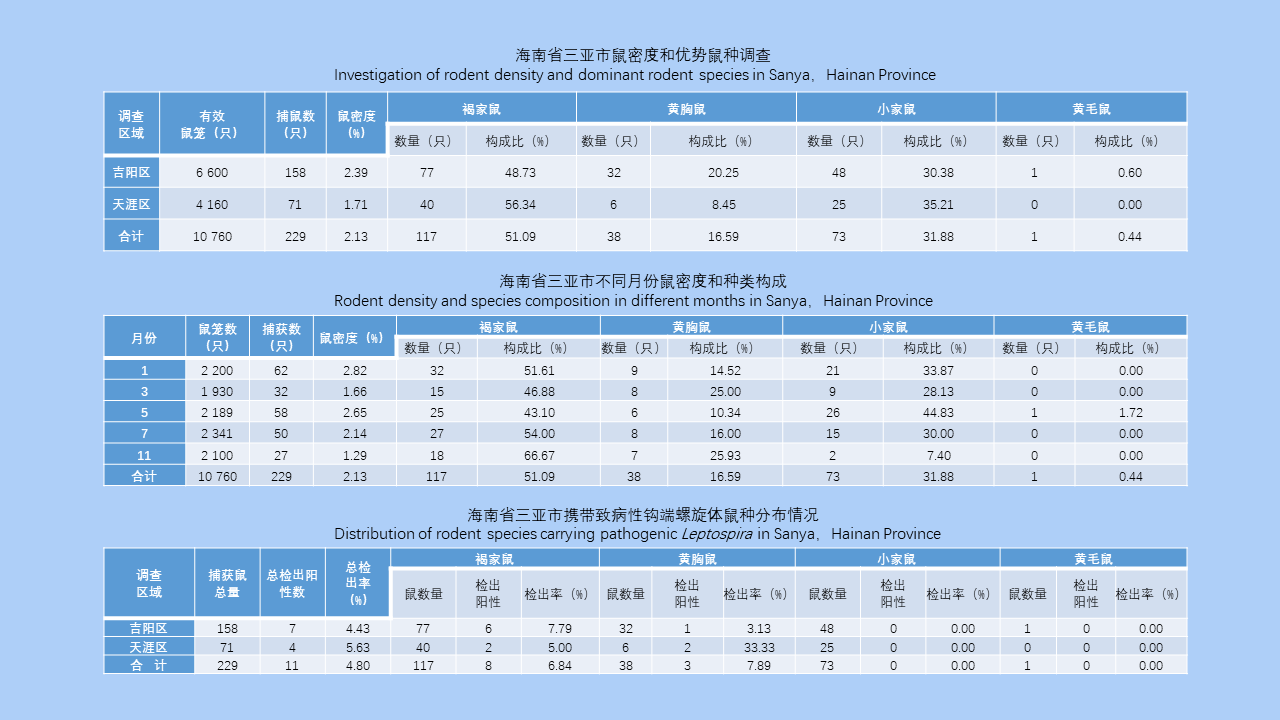
Objective To investigate the distribution of rodents and their pathogen infections in Sanya, Hainan Province, China, so as to provide a scientific basis for pre-warning, accurate prevention and control, and strategy development against rodent-borne diseases. Methods Rodents were captured in habitats such as residential areas, hotels, rural areas, and wild areas in Tianya and Jiyang districts of Sanya by deploying cages in the evening and harvesting in the morning (cage trapping using fried dough sticks as a bait). The rodents were morphologically identified, and aseptic dissection was performed. DNA and RNA were extracted from the liver, kidney, spleen, lung of the rodents. Taqman probe-based reverse transcription fluorescence quantitative PCR was used to detect pathogenic Leptospira, Orientia tsutsugamushi, Hantavirus, and Dabie bandavirus. The data were statistically processed using Excel 2021 and SPSS 26.0 softwares and analyzed by Chi-square test and Fisher's exact test between groups. Results A total of 10 760 effective cages were deployed, and 229 rodents were captured, with a rodent density of 2.13%. The rodent density was 1.71% (71/4 160) in Tianya District and 2.39% (158/6 600) in Jiyang District, with a significant difference between the two districts (χ2=5.785, P=0.016). The dominant species composition ratios were 51.09%, 31.88%, 16.59%, and 0.44% for Rattus norvegicus, Mus musculus, R. tanezumi, and R. losea, respectively. The peak rodent density was observed in January, May, and July. A total of 240 viscera samples from 229 rodents were tested, with pathogenic Leptospira detected in 16 samples (positive sample rate of 6.70% [16/240]). Specifically, positive rates for the kidney, spleen, liver, and lung of rodents were 18.52% (5/27), 8.33% (2/24), 7.50% (3/40), and 4.03% (6/149), respectively. Among the 11 rodents which tested positive for pathogens, with a positive rate of 4.8% (11/229), 4 were found to be positive for all the four organs. The highest detection rate of pathogens was found in R. tanezumi (7.89%, 4/38), followed by R. norvegicus (6.84%, 8/117), and M. musculus and R. losea (0 for both). The rodent infection rate was the highest in January, and the detection rate was 0 in March. There were significant differences in the rodent infection rate between months (P<0.001). None of Hantavirus, Dabie bandavirus, and Orientia tsutsugamushi was detected. Conclusions There is a relatively high risk of transmission of pathogenic Leptospira in Sanya, Hainan Province, and the rodent density is high. It is necessary to take targeted prevention and control measures to prevent the transmission of pathogenic Leptospira.