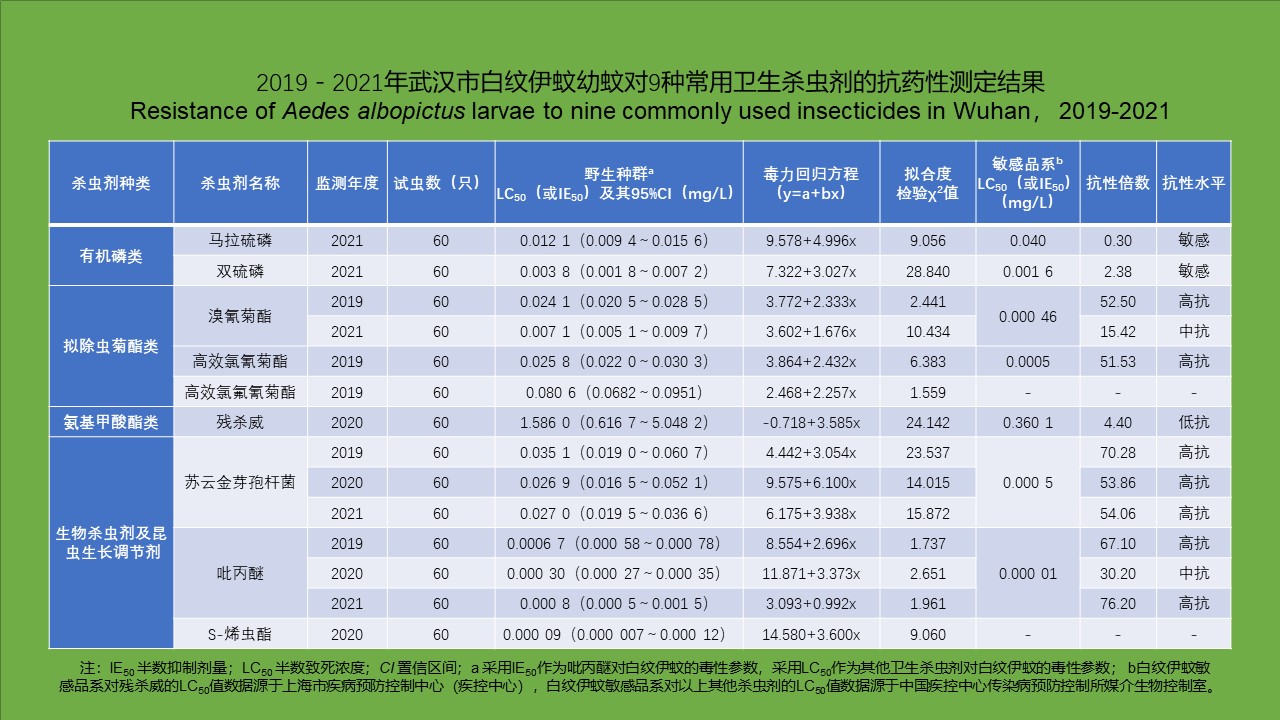
Biao DUAN, Si-xiang ZHANG, Cai-feng ZHAO, Mei HONG, Li-qiong SU, Wen-hong ZHAO, Zhi-ming YANG, Liang LU
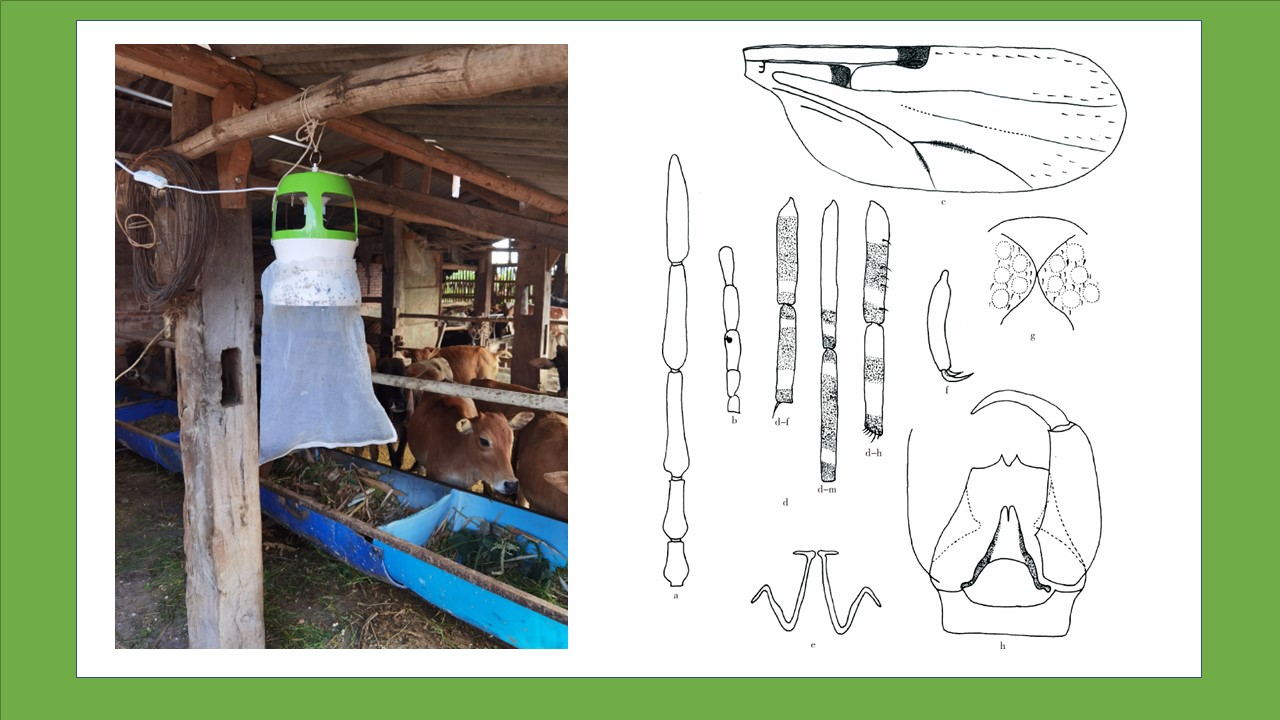
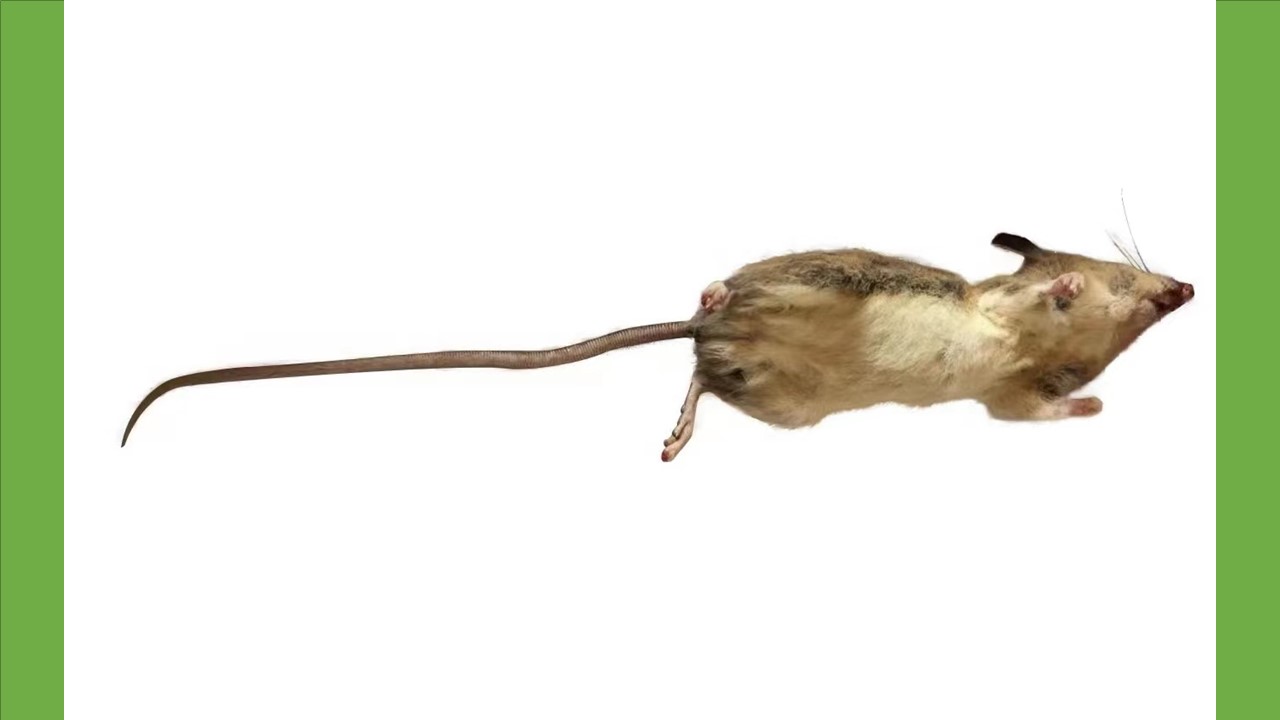
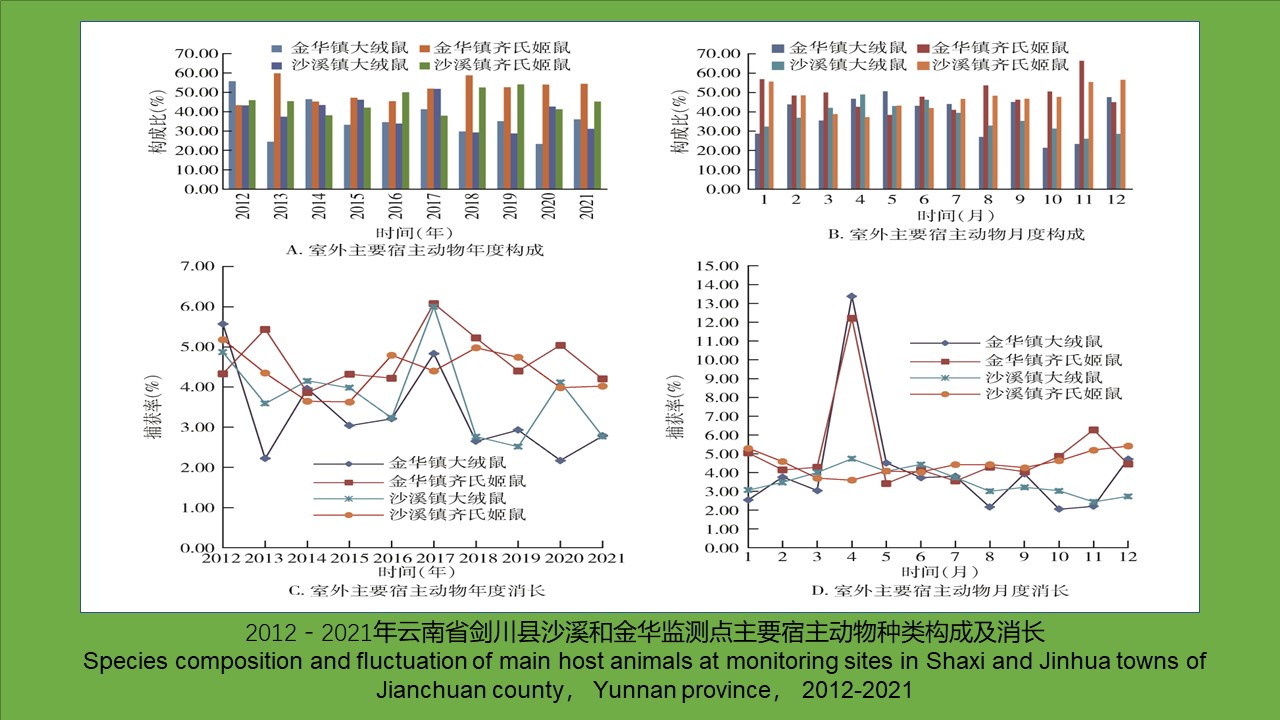
Objective To analyze the species composition and interannual and seasonal fluctuations of main host animals and flea vectors at historical and new plague foci in Jianchuan county, Yunnan province, China, and to explore the relationship between the population characteristics of hosts and vectors and plague epidemics. Methods Plague surveillance data were collected from Shaxi town surveillance point (historical) and Jinhua town surveillance point (new) in Jianchuan county, Yunnan province from 2012 to 2021. Descriptive and correlation methods were used to analyze the population characteristics of major host animals and fleas. Results The host animals found at Shaxi town surveillance point involved 22 species, 19 genera, 7 families, and 6 orders (outdoors:20 species, 18 genera, 7 families, and 6 orders; indoors:5 species, 4 genera, 2 orders, and 2 families). The host animals found at Jinhua town surveillance point involved 21 species, 17 genera, 6 families, and 5 orders (outdoors:20 species, 17 genera, 6 families, and 5 orders; indoors:10 species, 8 genera, 5 families, and 3 orders). The dominant species were Eothenomys miletus and Apodemus chevrieri at both monitoring sites, accounting for 37.73% and 45.90% in Shaxi town and 35.86% and 51.43% in Jinhua town, respectively. The fleas collected at the two surveillance sites involved 8 species, 8 genera, and 3 families (rodent body fleas:8 species, 8 genera, and 3 families; nest fleas:4 species, 4 genera, and 2 families). In Shaxi town, the body flea infestation rate was 28.91% (3 693/12 772), and the total flea index was 0.79 (10 144/12 772). In Jinhua town, the body flea infestation rate was 29.39% (959/3 263), and the total flea index was 0.71 (2 321/3 263). Frontopsylla spadix and Neopsylla specialis were the dominant species at both monitoring sites, accounting for 33.20% and 16.30% in Shaxi town and 36.49% and 19.09% in Jinhua town, respectively. Conclusion By comparing the population characteristics of main host animals and flea vectors at historical and new plague foci in Jianchuan county, it is indicated that the population characteristics of A. chevrieri and ectoparasitic F. spadix and N. specialis are more closely related to plague epidemics.