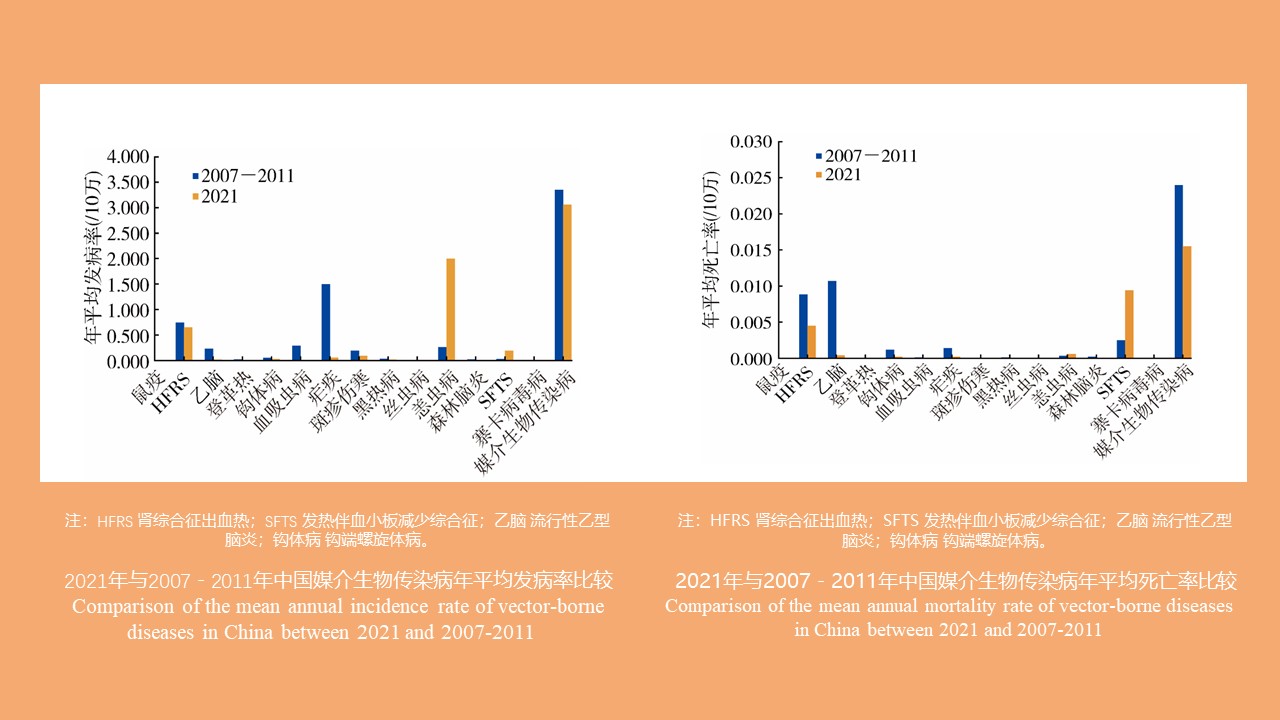
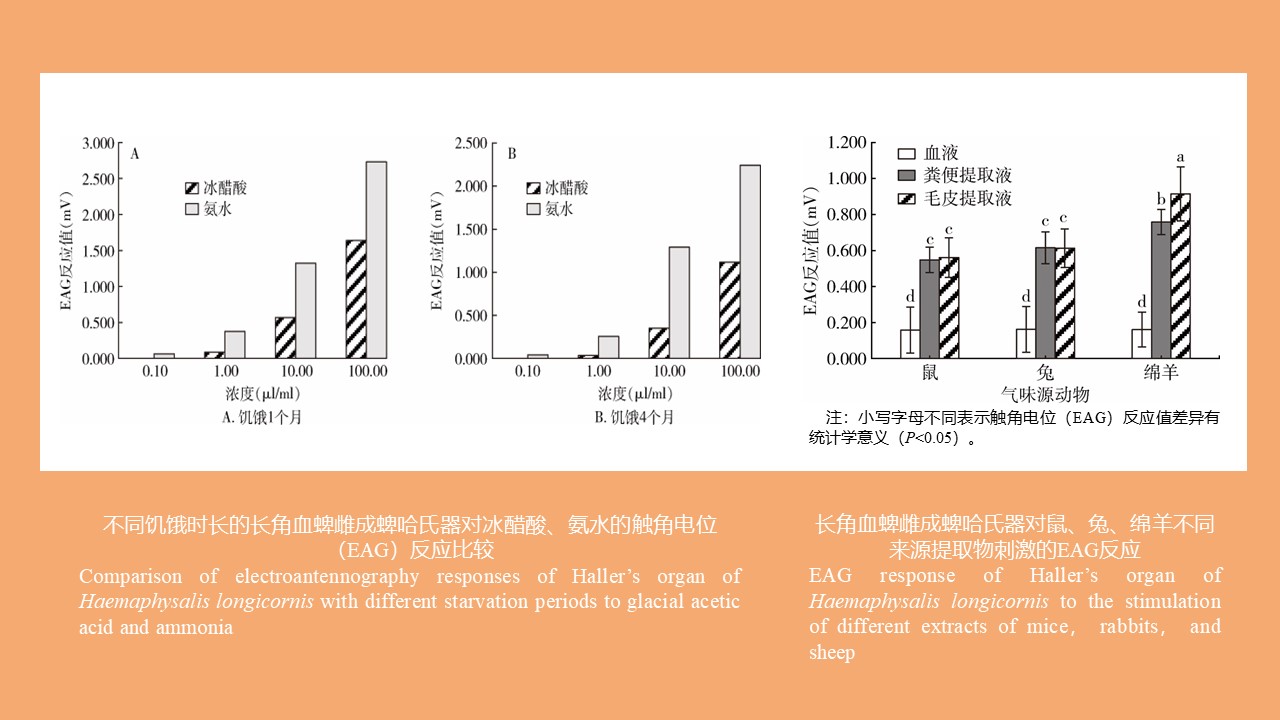
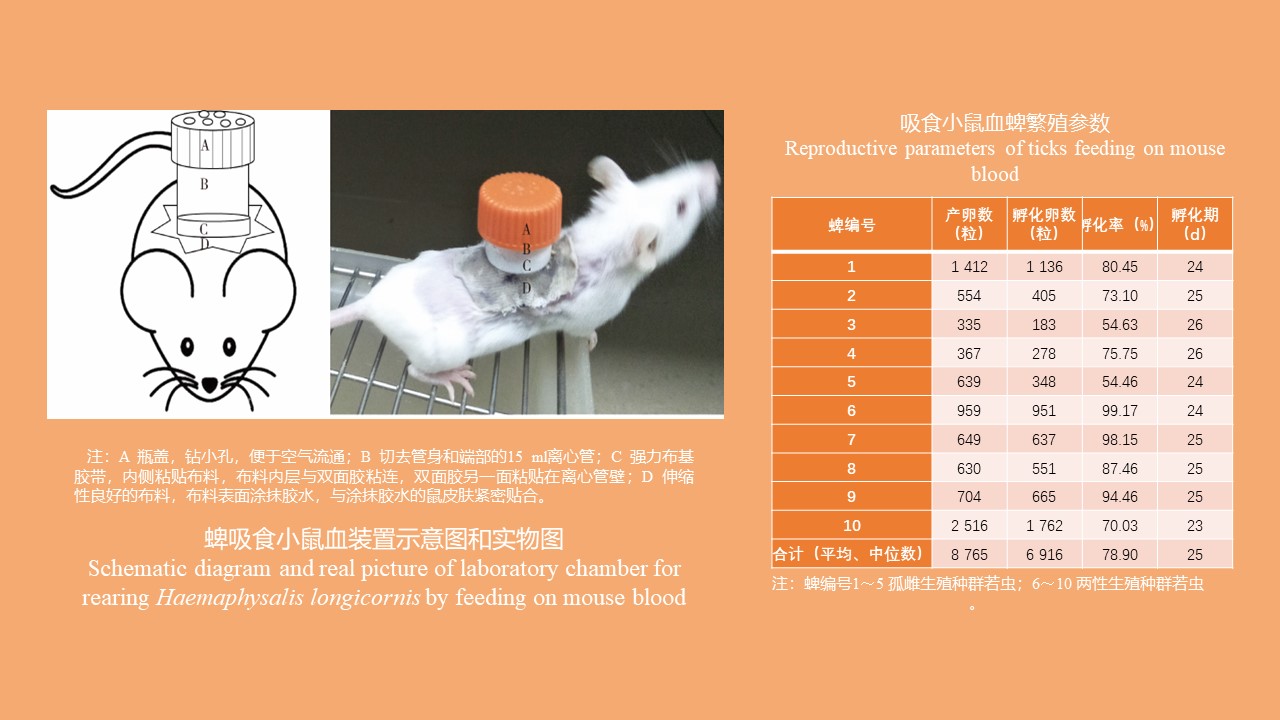
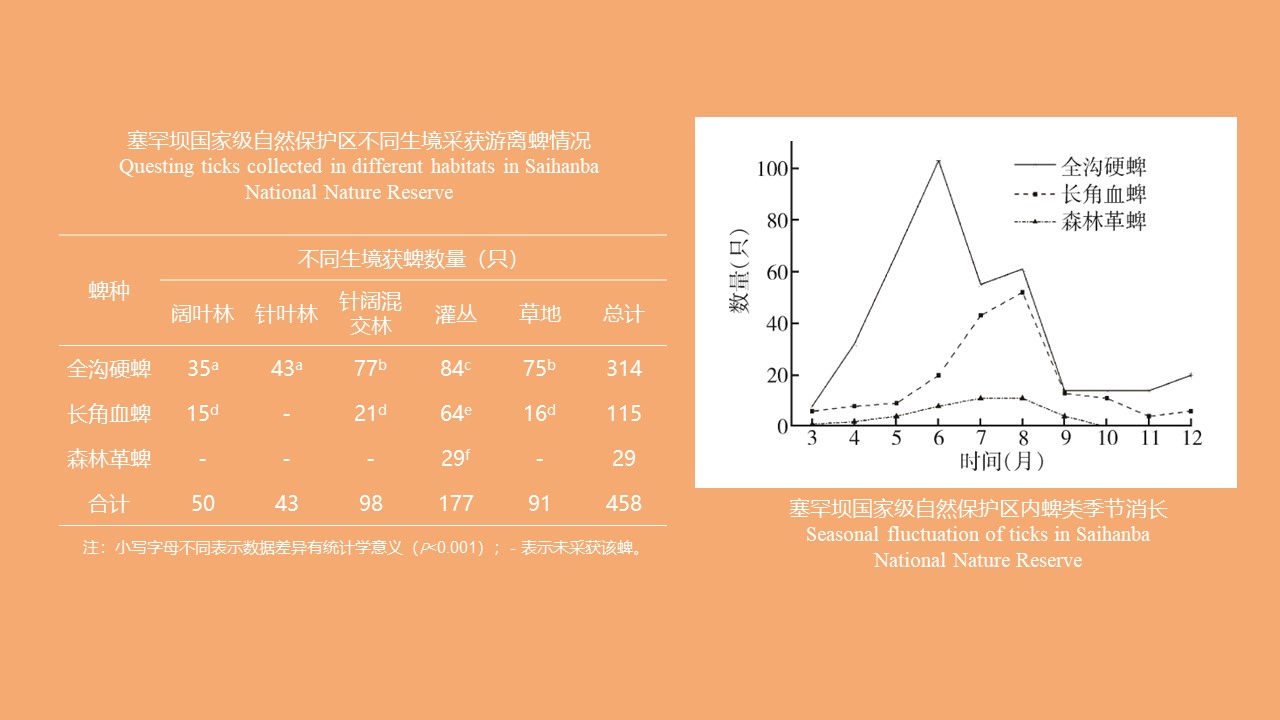
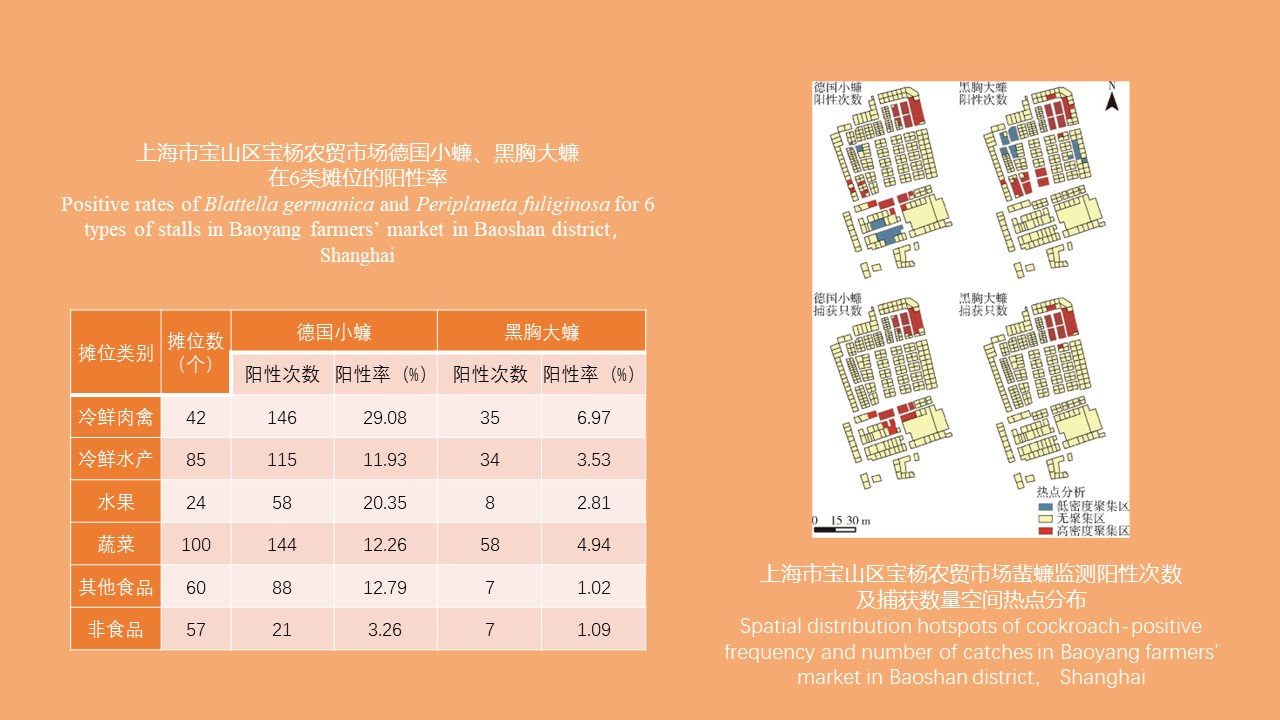
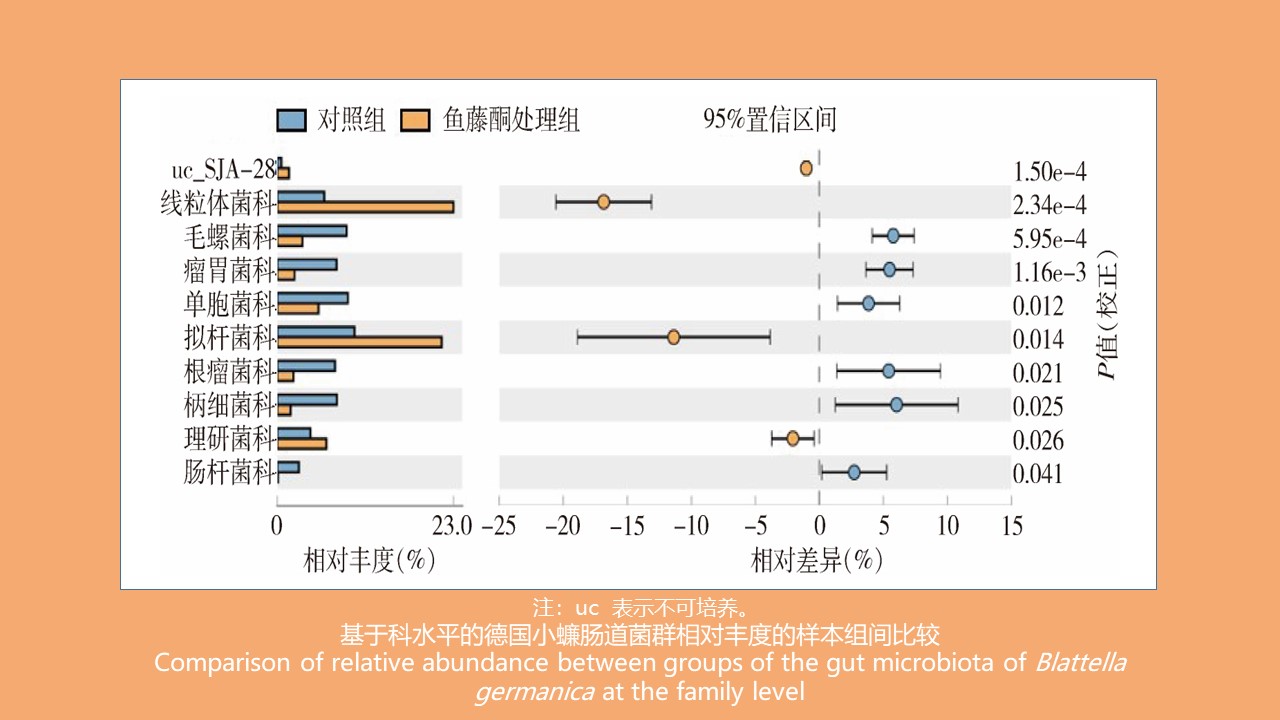
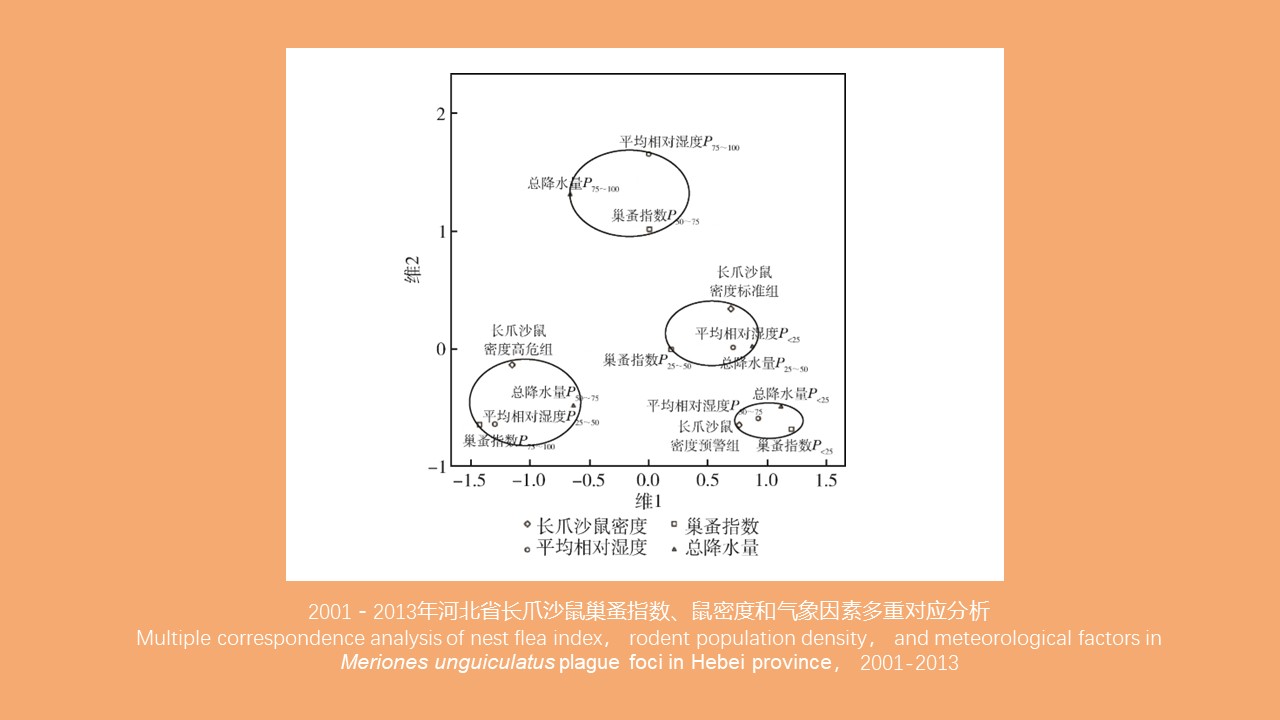
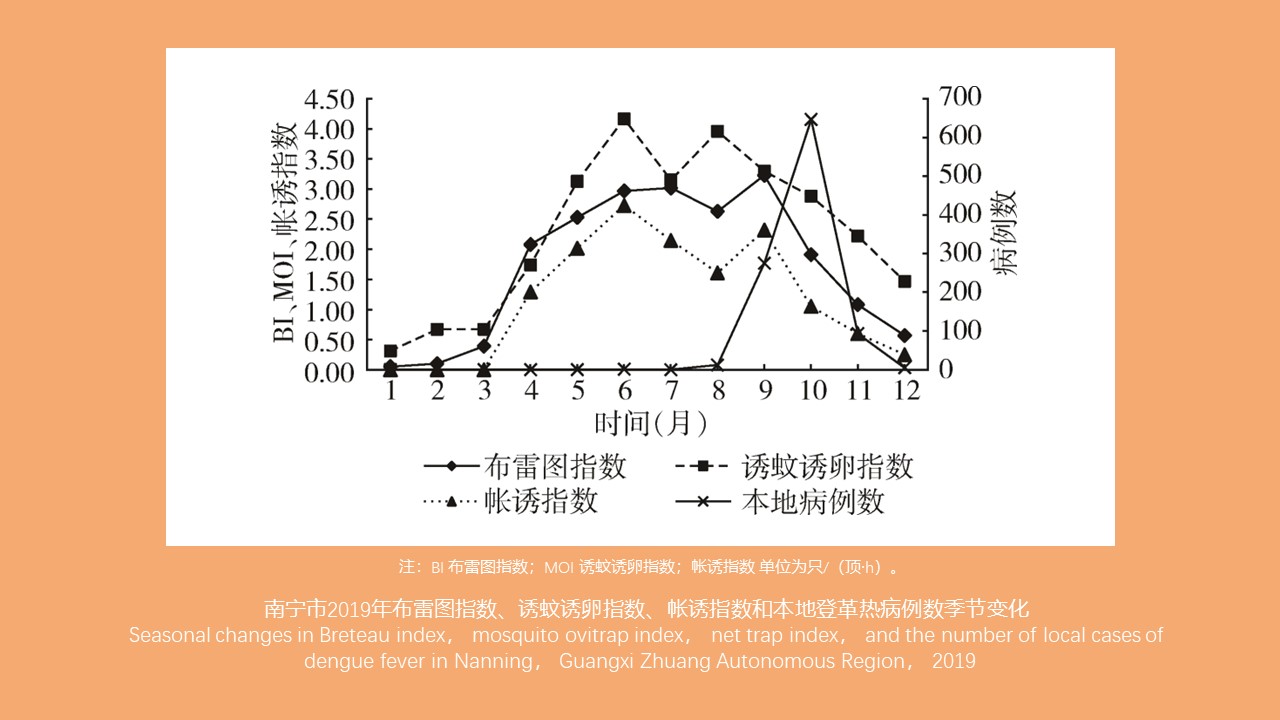
CAO Yang, WEI Ling-ya, JIN Hui, WANG Hui-min, KONG Qing-xin
Objective To explore a suitable temperature and method for short-term preservation of Aedes albopictus eggs in laboratory.Methods Ae.albopictus reared in the laboratory laid eggs.The eggs with complete and plump form were selected and counted under a stereomicroscope.Eggs in the control group were directly put into water for hatching after counting;eggs in the experimental group were divided into four groups according to the preservation time:7,14,21,and 28 d groups.Three repetitions were set in each group,and the number of mosquito eggs in each group was roughly equal.Eggs were preserved in constant temperature and humidity climate boxes with the humidity of 75% and the temperature was set to 5,10,12.5,15,20,and 25℃.After preserved for 7,14,21,and 28 days,eggs in the corresponding groups were taken out,observed with a digital microscope for the status and integrity,and hatched in water.When the earliest hatched larvae reached the 3rd instar,the observation ended.The larvae were counted,and the hatching rate was calculated.Excel 2019 software was used to sort out the data and calculate the hatching rate;SPSS 26.0 software was used for statistical analysis.The enumeration data were expressed as rate,and the measurement data in line with normal distribution were expressed as x±s.One-way analysis of variance was used for the comparison between two groups.Results As for the eggs of Ae.albopictus preserved at 5,15,and 25℃ for 7,14,21,and 28 days,respectively,the hatching rate of eggs preserved at 15℃ was 67.80% on the 7th day,50.00% on the 14th day,and remained about 50.00% on the 28th day;the hatching rate of eggs preserved at 5℃ decreased to 21.88% on the 7th day,9.32% on the 14th day,only 0.26% on the 21st day,and 0 on the 28th day.The hatchability of mosquito eggs stored at 25℃ was between the other two groups,and maintained at about 30.00% except for a significant decrease on the 14th day.There were significant differences in hatching rates of Ae.albopictus eggs stored at 5,15,and 25℃ for 7,14,21,and 28 days (7 d:F=36.688,P<0.001;14 d:F=166.749,P<0.001;21 d:F=7.890,P=0.021;28 d:F=19.501,P=0.002),and the hatching rates at 15 and 25℃ were higher than that at 5℃(except for 14-day preservation at 25℃)(7 d:P<0.001,P=0.033;14 d:P<0.001,P<0.001;21 d:P=0.008,P=0.033;28 d:P=0.001,P=0.007).As for the eggs of Ae.albopictus preserved at 10,12.5,and 20℃ for 7,14,21,and 28 days,respectively,the hatching rate of eggs preserved at 12.5℃ was 47.71% on the 28th day;the hatching rate of eggs preserved at 10℃ decreased gradually from the 7th day to 17.56% on the 28th day;the hatching rate at 20℃ was between the other two groups,and remained at about 40.00% on the 28th day.There was a significant difference in the hatching rate of eggs preserved at 10℃,12.5℃,and 20℃ for 14 and 28 days (14 d:F=23.700,P=0.001;28 d:F=9.429,P=0.014).The hatching rate at 12.5℃ and 20℃ were higher than that at 10℃(14 d:P<0.001,P=0.017;28 d:P=0.008,P=0.011).Conclusion When the environmental relative humidity is 75% and the egg-loading filter paper is always wet,12.5℃ and 15℃ are appropriate temperatures for short-term preservation of Ae.albopictus eggs.